Dental Dictionary

This Dental Dictionary aims to provide fundamental information about terms that may be discussed during your dental appointment. Talk to your dental staff if you need further clarification on these terms.
A
- Abscess – severe and persistent localized inflammation in the gum tissue or tooth root that causes infection, swelling, pain, and pus and can destroy neighboring teeth and bone if left untreated.
- Abutment—a natural tooth or dental implant that supports a fixed or removable dental prosthesis
- Acid etching—preparing dental enamel or dentin for bonding with an acidic chemical.
- Acrylic resin—used to make artificial teeth and crowns.
- ADA – American Dental Association, an organization of US dentists noted for public dental health education.
- Adhesion—chemical or physical factors connecting two or more surfaces without adhesive—is part of bonding.
- Adhesive—any material that permanently bonds two or more surfaces.
- Air abrasion—blasting air and abrasive material at a tooth to remove small pieces of tooth structure.
- Alloy/amalgam – a combination of two or more elements with unique qualities
- Alveolar – tooth-anchored jawbone.
- Anesthesia—medication that blocks pain in one region for treatment
- Anesthetic (general) – drugs that put patients to sleep during therapy.
- Anterior—teeth or tissues in the mouth’s front.
- ANUG – Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis, gum ulcers caused by stress or smoking.
- Apicoectomy—surgical root amputation for dead teeth
- Appliance—braces, mouthguards, or retainers
- Arch—curved upper or lower dental structure
- Archwire—braces metal wire that aligns teeth.
- Arthrogram—a diagnostic x-ray that injects contrast dye into the joint to view bone structures
- Artificial crown—prosthetic tooth restoration that covers or replaces a tooth and may attach to a partial tooth or dental implant.
- Attrition—natural wear destroying structure
- Augmentation—treats soft tissue or bone insufficiency
B
- Band—metal ring bonded around a tooth to fasten brackets.
- Banding—fitting and gluing orthodontic bands to teeth
- Base—insulating material under restorations to protect tooth pulp from temperature variations
- Benefit—third-party insurance pays for dental services
- Benign—mild, non-threatening, or non-malignant
- Bicuspid—tooth in front of molars and behind cuspids
- Bilateral—indicates both sides
- Biopsy – removing a small piece of tissue for testing.
- Bioinert—a material that does not promote inflammation or immunological response.
- Bite/occlusion—the physical connection between upper and lower teeth when closed
- Bleaching—whitening teeth with chemical oxidizers or lasers
- Block injection – anesthetic to numb a big jaw and mouth area.
- Block graft—screw-stabilized bone graft used to repair major bone defects
- Bonding two surfaces, orthodontic appliance seal
- Bonding—attaching brackets for orthodontics or repairing teeth with composite resin to change color or shape.
- Braces – brackets, and archwires used to realign teeth gradually.
- Bracket – ceramic or metal plate glued to the tooth to hold an archwire for orthodontic treatment
- Bridge/partial false teeth – dental prosthetic device that supports one or more missing teeth by attaching to adjacent teeth or implants.
- Bruxism—involuntary teeth grinding, commonly while sleeping, causes tooth wear, sensitivity, migraines, and jaw pain.
- Buccal: cheek-related
C
- Comprehensive dental services
- Caring and compassionate dentists
- Customized treatment plans
- Cutting-edge dental technology
- Convenient appointment options
- Clean and comfortable clinic
- Certified dental professionals
- Cost-effective dental solutions
- Community-oriented dental care
- Cosmetic dentistry expertise
- Child-friendly dental services
- Continuing education for dentists
- Commitment to patient safety
- Clear communication with patients
D
- DDS – is identical to DMD.
- Debridement—removing plaque and calculus that hinders evaluation
- Demanding—removing cemented orthodontic bands from teeth
- Debonding—removing glued orthodontic brackets from teeth
- Deciduous teeth—”baby” or “primary” teeth—arrive between birth and three and fall out as permanent teeth sprout.
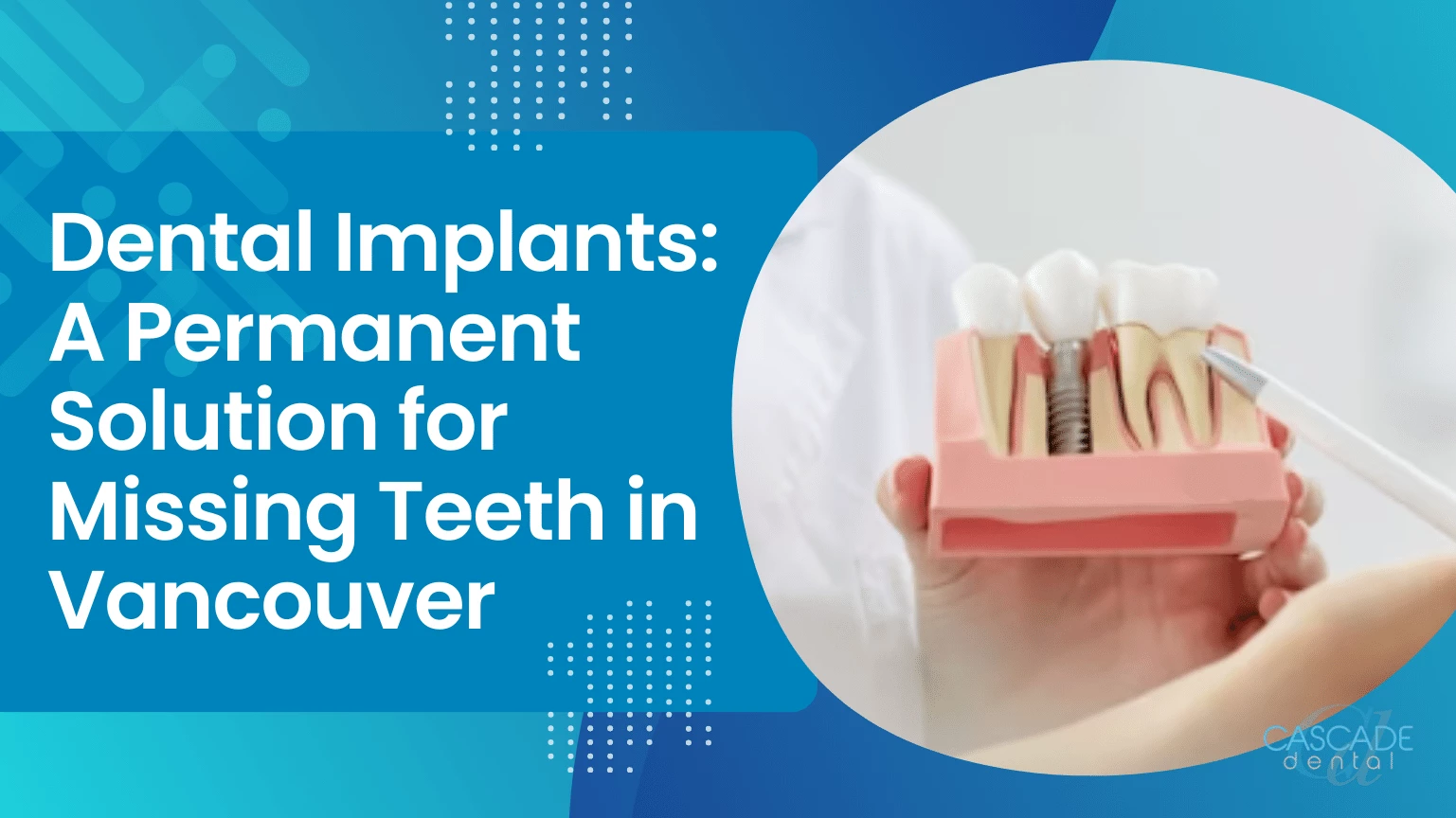
- Dental implant—small titanium cylinder placed into the upper or lower jawbone to anchor a dental device or restoration.
- Dentin—the tooth’s hard inner layer beneath the enamel—makes up most of its structure.
- Dentists evaluate, diagnose, prevent, and treat illnesses and problems of the teeth, mouth, gums, jaws, and other oral and maxillofacial areas.
- Dentition—the mouth’s teeth
- Diagnostic cast—impression for treatment planning
- Diagnostic imaging—photographs or radiographs for diagnosis
- Diastema—the gap between two teeth
- Discectomy—joint disc removal
- Dropped tooth – tooth that has grown or shifted out of place.
- Distal—tooth part farthest from the arch
- DMD is equivalent to DDS.
- Dressing—medicines, bandages, or other materials used to facilitate wound healing
- Dry socket — painful tooth socket inflammation following extraction caused by infection or loss of the blood clot needed for recovery.
E
- Edentulous—without teeth
- Enamel—hard tissue covering the dentin
- Endodontics—dental specialty treating tooth pulp and related areas
- Endodontists treat tooth pulp disease and trauma.
- Epidemiology—the study of population disease incidence and prevalence
- Equilibration—reshaping bite surfaces to address the imbalance, also known as occlusal adjustment
- Eruption—teeth emerging from gums
- Evulsion/avulsion—traumatic tooth extraction
- Excision—surgically removing tissue or bone
- Exodontia—dental extraction
- Exostosis—bone overgrowth
- Extraoral—outside the mouth
- Extra coronal—the tooth’s outer crown
- Exudate—fluid, cells, and debris from necrosis or inflammation
- Eyeteeth—cuspid or “canine” teeth
F
- Family-friendly dental care
- First-rate dental services
- Friendly and experienced dentists
- Flexible appointment scheduling
- Fast and efficient treatments
- Full range of dental procedures
- Fear-free and comfortable environment
- Focused on patient satisfaction
- Finest dental technology and equipment
- Fair and transparent pricing
- Free dental consultations
- Follow-up care and support
- Fostering dental health education
G
- Gentle dental treatments
- Great patient reviews
- General dentistry services
- Gifted and skilled dentists
- Germ-free and sanitized environment
- Guidance on oral hygiene
- Guaranteed customer satisfaction
- A growing list of happy patients
- Generous discounts and promotions
- Goal-oriented treatment plans
- Genuine care for each patient
- Groundbreaking dental technology
- Global approach to dental care
- Giving back to the community
H
- High-quality dental care
- Highly trained and experienced dentists
- A holistic approach to dental treatments
- Hygienic and sanitized clinic
- Hassle-free appointment scheduling
- Honest and transparent communication
- Happy and satisfied patients
- Home-like atmosphere
- Helpful and friendly staff
- Healing-focused dental procedures
- High-tech dental equipment
- Human-centric dental services
- Health-conscious dental solutions
- HSA and insurance accepted
I
- Innovative dental treatments
- Impeccable dental hygiene
- Individualized patient care
- In-house dental specialists
- Infection control measures
- Insurance assistance provided
- Immediate dental emergency care
- Impressive dental technology
- An inclusive and welcoming atmosphere
- Interactive patient education
- International standards of care
- Integrity-driven dental practice
- Invested in patient satisfaction
- In-network with major insurance providers
- Informative dental consultations
- International patients are welcomed
J
- Judicious treatment recommendations
- Joyful and relaxed dental experience
- Joint pain relief solutions
- Judgment-free dental care
- A journey towards optimal oral health
- Just-in-time appointment availability
- Jovial and professional staff
- Journal-worthy dental results
- Jitter-free dental procedures
- Jaw alignment assessments
- Jargon-free explanations
- The juxtaposition of art and science in Dentistry
- Joyful smiles restored
- Juggling dental care with busy schedules
- Jaw-dropping smile makeovers
K
- Knowledgeable dentists and staff
- Kind and compassionate care
- Kid-friendly dental environment
- Key focus on patient comfort
- Keen attention to dental details
- Keeping up with dental advancements
- Kick-starting dental health journeys
- Knowledge-sharing with patients
- Knockout cosmetic dentistry
- Knowledgeable guidance on oral hygiene
- Keeping dental treatments affordable
- Kudos from satisfied patients
- Kosher dental practices
- Keeping smiles radiant and healthy
- Kindness and respect toward patients
L
- Laminate veneer — thin, tooth-colored material used to cover the front of a healthy tooth to fix discoloration, damage, misalignment, or other cosmetic issues.
- Laughing gas is nitrous oxide, an odorless gas that induces slight sedation.
- Lesion—tissue damage through trauma, infection, or disease
- Ligation Orthodontic attaches archwire to braces.
- Ligature—thin wire used to hold the archwire in orthodontic brackets
- Lingual – tongue surface, opposite facial.
- Lip bumper—archwire attached to molded plastic pulls back lower jaw molars to make room for additional teeth
- Local anesthesia—medication that blocks nerve impulses to relieve pain during treatment.
M
- Malocclusion—misaligned teeth or jaws
- Mandible—lower jaw
- Mandibular canal – mandible’s blood vessels and nerves for the lower jaw and teeth.
- Mastication—chewing food
- Maxilla—upper jaw
- Maxillary sinus (maxilla cavity)
- Molar – back teeth, cusped, grind food
- Mouth guard—protects teeth and mouth during sports.
N
- NSAID – an abbreviation for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a type of pain treatment.
- Night guard – a device that can protect your teeth and jaw while you sleep if you grind your teeth.
- Nitrous oxide, more commonly called laughing gas, is an odorless inhalant with a calming yet mildly sedated effect.
O
- Occlusion—the arrangement of upper and lower teeth when the mouth is closed, also called “bite.”
- Onlay – prosthetic repair that covers a tooth’s occlusal (biting/chewing) surface but not the full tooth.
- Operculectomy—surgically removing the operculum
- operculum—tissue flap covering a partially or entirely unerupted tooth
- Oral: mouth
- Oral and maxillofacial surgery includes extraction, repair of deformities or fractures, removal of tumors or cysts, and others.
- Oral hygiene—habits that maintain teeth, gums, and mouth healthy
- Oral pathologists research, diagnose, and treat illnesses of the mouth, jaws, and related areas.
- Oral pathology—study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the mouth, jaws, and related areas
- Orthodontics—dental specialty that diagnoses, prevents, and treats malocclusion and other orofacial neuromuscular or skeletal problems.
- Orthodontists diagnose, prevent, and treat malocclusion and other orofacial neuromuscular or skeletal disorders.
- Orthognathic—the functional link between the mandible and maxilla (upper and lower jaws)
- Osseous—bone tissue
- Osteoplasty—bone-remodeling surgery
- Osteotomy—bone-cutting surgery
- Overbite—an orthodontic condition when the upper front teeth greatly overlap the lower.
R
- Radicular—tooth root
- Radiograph (x-ray) — ionizing radiation imaging of bone and teeth structures.
- Reimplantation—replacing a tooth after trauma.
- Reline—resurfacing the tissue side of a removable artificial teeth to improve fit.
- Resin: dental restoration material
- Resorption—bone loss
- Retainer—a device used to keep teeth aligned after orthodontic treatment
- Root – tooth part that connects to gums and socket
- Root canal—tooth pulp cavity
- Root canal therapy—removal of pulp and replacement with inert material—treats tooth pulp disease or injury.
- Root planing—a periodontal disease therapy that deep cleans dental roots to eliminate calculus and other impurities.
- Rubber dam—latex sheet used to shield the area of the mouth from saliva and pollutants during surgery
S
- Scaling—professional deep cleaning to remove plaque, calculus, and surface stains from teeth, typical periodontal disease treatment
- Sealant—thin, resinous substance placed to rear molar occlusal surfaces to prevent deterioration
- Separator/spacer—small rubber orthodontic ring used to space teeth before bands are joined
- Sinus graft—maxillary sinus bone graft for dental implants
- Sleep apnea—airway collapse interrupts sleep.
- Space maintainer — dental appliance used to fill prematurely lost baby tooth space to prevent neighboring teeth from moving.
- Stomatitis—mouth membrane inflammation
T
- Tartar—dental calculus, hard, rough layer on teeth that draws plaque
- Temporomandibular joint disorder/dysfunction (TMD)—jaw and facial pain and restricted movement.
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)—hinge between lower jaw (mandible) and skull base
- Treatment plan—doctor-patient agreement on oral health treatments
- Trench mouth—gum disease with severe mouth ulcers, tissue loss, and halitosis
U
- Usual normal, customary, and reasonable (UCR) fee: a procedure’s price is decided by consensus.
- Unerupted tooth—tooth that has not yet emerged from the gum.
V
- veneer—thin facing glued to the front of a tooth to improve the appearance
W
- Wax can reduce braces irritation.
- Wire tie—fine wire that twists around the bracket to retain the archwire in bracing.
- Wisdom teeth, the third and last set of back molars, usually emerge between 18 and 25.
At Cascade Dental, we are dedicated to providing all of our patients with the highest possible quality of service at all times. Our attitude is that the foundation of outstanding dental treatment is a personal relationship between the patient, the dentist, and other dental care team members. As a result, each treatment is customized to fit your one-of-a-kind requirements and go above and beyond your expectations.